What is an IC Board?
IC boards, integral to electronics, integrate circuits on PCBs, offering cost-effectiveness, miniaturization, and versatility across various technologies.
With regard to electronics, the IC board can be identified as an important part of the foundation on which technological advancements in integrated circuits are built. It is also referred to as one type of Printed Circuit Board Assembly, hence abbreviated as PCBA. An IC board merely refers to the integration of complicated circuits within a compact device that allows numerous electronic functions. This article takes a closer look at IC boards, their parts, applications, and other aspects that make them quite essential in many forms of technology.
The Structure of IC Board
The IC board, which is essentially a PCB, has integrated circuits, or ICs, installed on it. In essence, interconnecting wires provide electrical connections from the integrated circuits (ICs) to the board surface when they are joined. A sensible and reliable way to regulate electrical impulses between devices is offered by this configuration.
The non-conductive substrate that makes up an IC board's mechanical structure is covered with copper channels and is often composed of fiberglass or epoxy. The complex networks created by these copper traces allow current to move between the numerous implanted parts, including as connectors, resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors.
How IC Boards Work
IC boards operate by integrating components through an interconnecting network. The size and shape of these boards differ according to specific design needs; however, they all have one thing in common: the presence of interconnecting wires that integrate the electrical components. For this to take place, mechanical support is quite vital since it aids in supporting the internal and external wires in position, normally by structural support from the board or an external framework itself.
The brilliance of IC boards lies in their structured pathways that prevent the unintentional electrical connection of components. These channels are crucial to a board's functioning because they direct electrical current where it is needed. Without them, such capability would completely disappear.
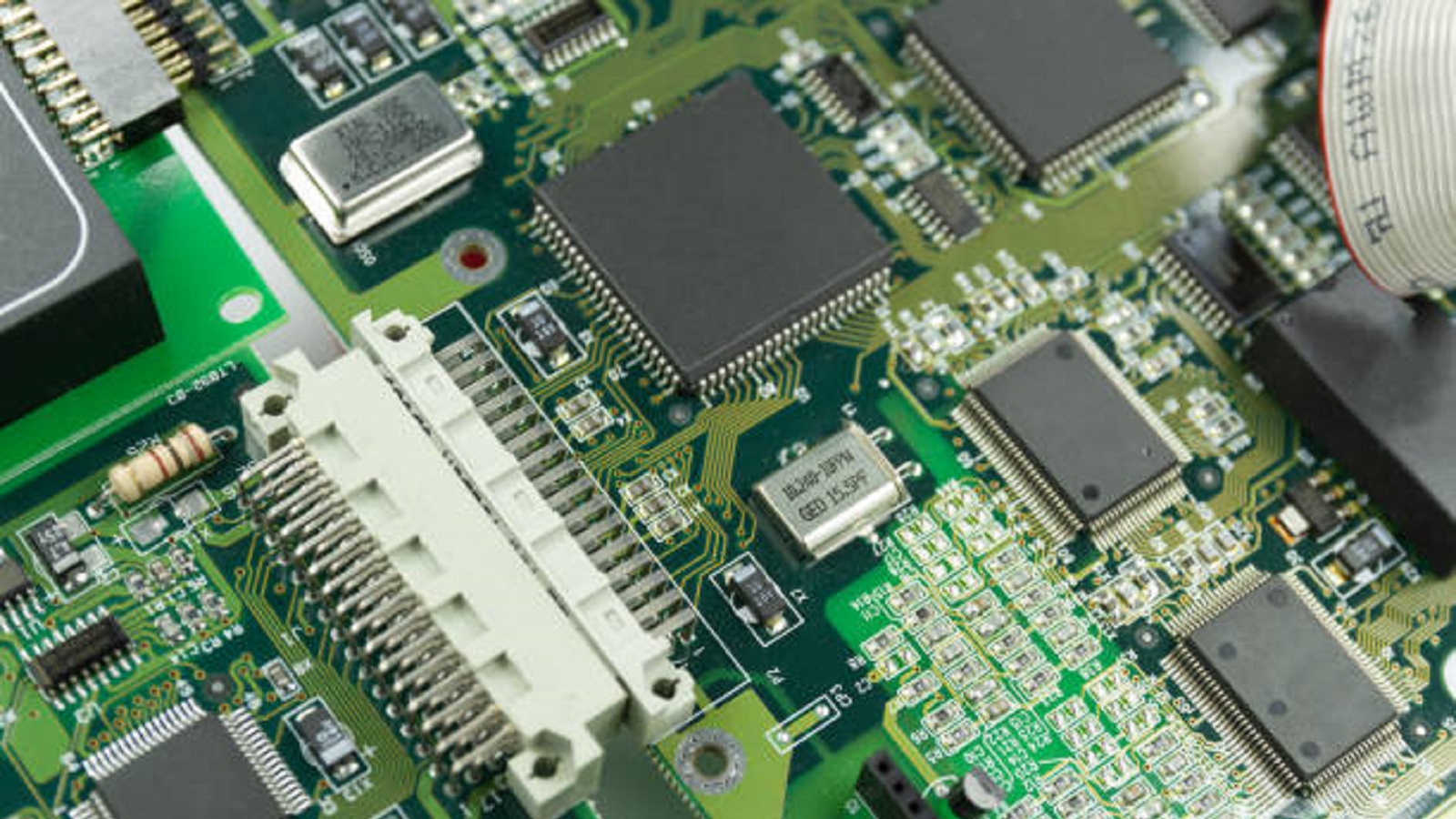

Types of IC Mounting Methods
IC boards use a range of mounting techniques for its component elements, such as:
Surface Mount Technology: This cutting-edge method installs parts directly onto the surface of the board. SMT is useful and widely used in products where compactness is essential since it saves space.
Through-Hole Technology: This method involves feeding component leads via board holes and is less common than SMT. It is used in circumstances that need strong mechanical bonds, which usually arise in high-stress environments.
Hybrid Approach: It offers flexibility by integrating through-hole and surface mount methods to connect several components on a single board.
Applications and Benefits
These are carried by high-power computers, enormous industrial machines, and electronic appliances. Their demand arises due to the following reasons:
Multi-Purpose: IC boards are employed from microcontrollers in automobiles to significant modules in medical devices. Microcontrollers on an IC board are tiny computers that run consumer electronics; they are used to control medical devices and automate industrial processes.
Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their inexpensiveness, IC boards can be utilized for both consumer and commercial applications requiring mass production and integration into various devices.
Miniaturization and Reliability: The use of IC boards realizes high-density component architectures that make these gadgets even smaller without necessarily compromising functionality or strength. This component has revolutionized computing by making it easier to create small yet powerful machines.
Scalability for Industrial Applications: The modular architecture of the IC boards makes it easy to integrate into larger systems and scale for industrial applications requiring inter-device connectivity.
Common Elements on IC Boards
The numerous elements present on the IC boards serve a particular purpose, including:
Microcontrollers and Microprocessors: These constitute the central controlling part of a device.
SMDs (Surface Mount Devices): Logic circuits and memory constitute this group, which are very space-efficient.
BGA: Which are used in high-performance computers due to their reliability.
QFP: Quad Flat Packs are used in advanced electronic devices such as mobile phones.
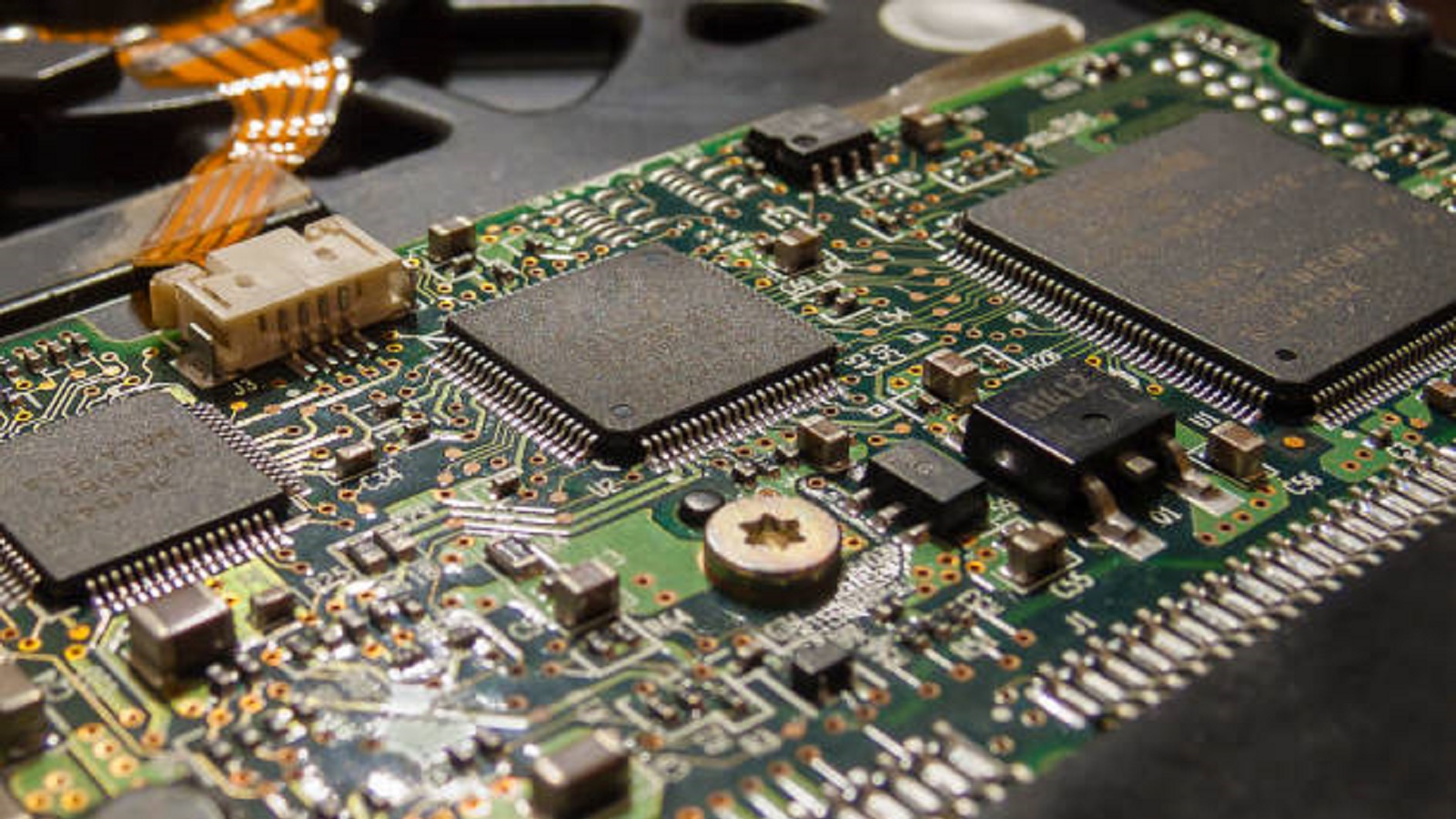
All these components collectively make the work of IC boards very complex, functioning in various fields. The IC board is a technological marvel that has constantly projected the future of electronics. It plays the role of an integration platform of circuits that has facilitated unmatched development in many fields, right from daily applications to specialized use in industry. PCBX recognizes the importance of IC boards and is devoted to providing top-tier solutions that match the changing demands of modern technology, from production to assembly, while keeping quality and precision at the forefront of innovation. Request a quote for PCB manufacturing and assembly today and join the next wave of electronic design and integration.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
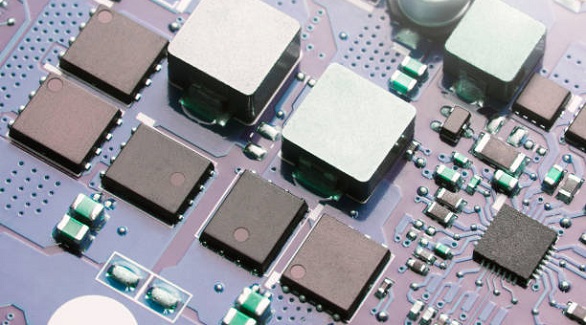
eFuses are advanced PCB fuses that reset automatically, offering fast, precise protection and versatility in electronics, enhancing device safety and reliability.
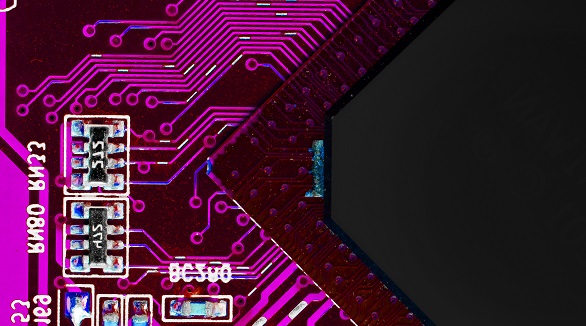
High-speed PCBs (>1GHz) are crucial for advanced electronics like 5G and data processors. Key practices include ensuring signal integrity, controlling EMI, and maintaining power integrity for reliable performance.
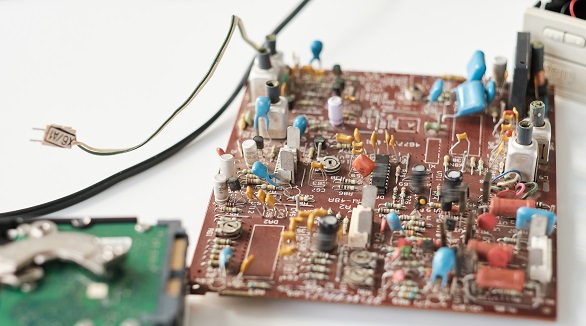
Capacitors are crucial in circuits for storing energy. Testing methods include in-circuit and out-of-circuit using digital multimeters, ESR, and LCR meters. Proper testing ensures reliability and prevents malfunctions.
